Overview:
Diabetes Mellitus commonly known as diabetes is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar. It is a disease in which your glucose or sugar levels are too high in the blood-stream. In such a condition, your body either doesn't make enough insulin or can't effectively use the insulin it does make.
If left unchecked, this condition can cause several health complications in the short-term as well as long-run. In the short-run, the patient is risking serious health problems which can potentially cause death, and in the long run, it can result in cardiovascular diseases, cause damage to the kidneys or the eyes, and in some cases cause cognitive impairment.
Diabetes can occur as a result of the pancreas not producing insulin, or the cells in the body do not react properly to the insulin. Insulin is created in the pancreas that breaks the glucose levels in the blood-stream and provides energy to the cells. When it stops producing or does not react correctly, it will result in diabetes.
Types of Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the body stops producing insulin and so the glucose levels keep rising in the blood. Over time the high glucose levels will lead to more health problems such as nerve damage, kidney failure, heart problems, and eye damage.
The loss of beta cells results in type 1 diabetes. This occurs due to an autoimmunity response. Autoimmunity refers to the immune cells responding against the body’s own healthy cells and tissues. The reason for autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes is yet unknown.
Type 1 can occur at any time in people irrespective of age. Whether it's children or young adults, they will likely get type 1 diabetes should they encounter problems.
Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the body not only stops producing insulin but doesn’t use insulin well enough either. The cells in the body do not respond properly to the insulin, and so the glucose levels will keep increasing. Eventually, insulin production stops and the patient may need to take insulin through syringes in order to make up for the lack of production.
Should the sugar levels remain too high, it leads to several health problems related to the heart, kidneys, and nerves. And also vison.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type that occurs mostly in older people. It is also hereditary and can be inherited through genetics. People who are obese and have an unhealthy lifestyle are at a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Lack of exercise and a sedentary lifestyle is a leading cause of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
The third type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy. Women who don’t have a history of diabetes develop high glucose level during pregnancy. Unlike type 1 and type 2, gestational diabetes goes away after childbirth, however, the child in question is affected by the diabetic condition, and the mother is also at risk of getting type 2 if not careful.
Gestational diabetes has two classes, namely A1 and A2. Women diagnosed with A1 can manage their diabetic condition through exercise and diet, while women with A2 will need to manage by taking insulin and other medication.
If left untreated, or poorly treated, the child born is at risk of having quite a few health problems. Low blood sugar, jaundice, or are born larger than normal. In some cases, the child may be stillborn. On the other hand, the mother may be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The cause of the three types of diabetes may be different, but they mostly have the same symptoms. The overall symptoms are:
-
Increased appetite
-
Frequently urinating
-
Feelings of exhaustion
-
Frequent thirst
-
Blurry vision
-
Sores appear over the body and do not heal altogether or heal slowly
-
Loss of weight
Of course, there are a few minor differences in symptoms of the three types which are elaborated here.
Type 1
For Type 1 diabetes, the symptoms are:
-
You will lose weight even if you haven’t planned to. This occurs due to a lack of energy since no insulin means no glucose energy. Therefore, the body absorbs muscle fiber, and fat to gain more energy which leads to weight loss.
-
Nausea. You will experience nausea and vomit to the build-up of ketones because of the burning fat. This can lead to a serious life-threatening disease known as diabetic ketoacidosis.
Type 2
For Type 2, the symptoms are:
-
Itchy, dry skin
-
Pain in your feet, or complete numbness
-
Unexpectedly gain weight
-
A decreased vision
-
Sores and cuts heal slowly
-
Yeast infections
Gestational Diabetes
For gestational diabetes, there are no specific symptoms. You may feel thirstier and hungrier and urinate more often. Please note that gestational diabetes occurs in women who don’t have a history of diabetes, but experience high glucose levels during pregnancy.
Treating and Managing
For now, in human history, there is no real cure for diabetes mellitus, but there are ways to control it and live with it. In fact, many people with diabetes are able to live a long healthier life with the right diet control, and keeping their sugar level in check.
Diabetes cannot be cured nor can it be completely prevented, it is only delayed with the correct lifestyle, diet, and in some cases, medication can also be used.
Here are some ways you can control your diabetes and live a healthier and happier life:
Exercise
Exercising regularly to burn the glucose levels in the blood-stream. With enough physical activity, the insulin hormones become more sensitive and are better at using the energy from the high glucose levels. Thus your sugar levels remain stable and do not build up.
Hydration
Stay hydrated by drinking water whenever you can. Doing so will decrease the glucose levels in the blood, which are flushed out through urine. It also keeps your kidneys healthy and in a good shape.
Manage your carbs
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and then they are moved into cells by insulin. You will encounter problems if there are too many carbohydrates in your diet, or insulin production is low, and end up with diabetes. Therefore, it is advised to control the number of carbohydrates you consume.
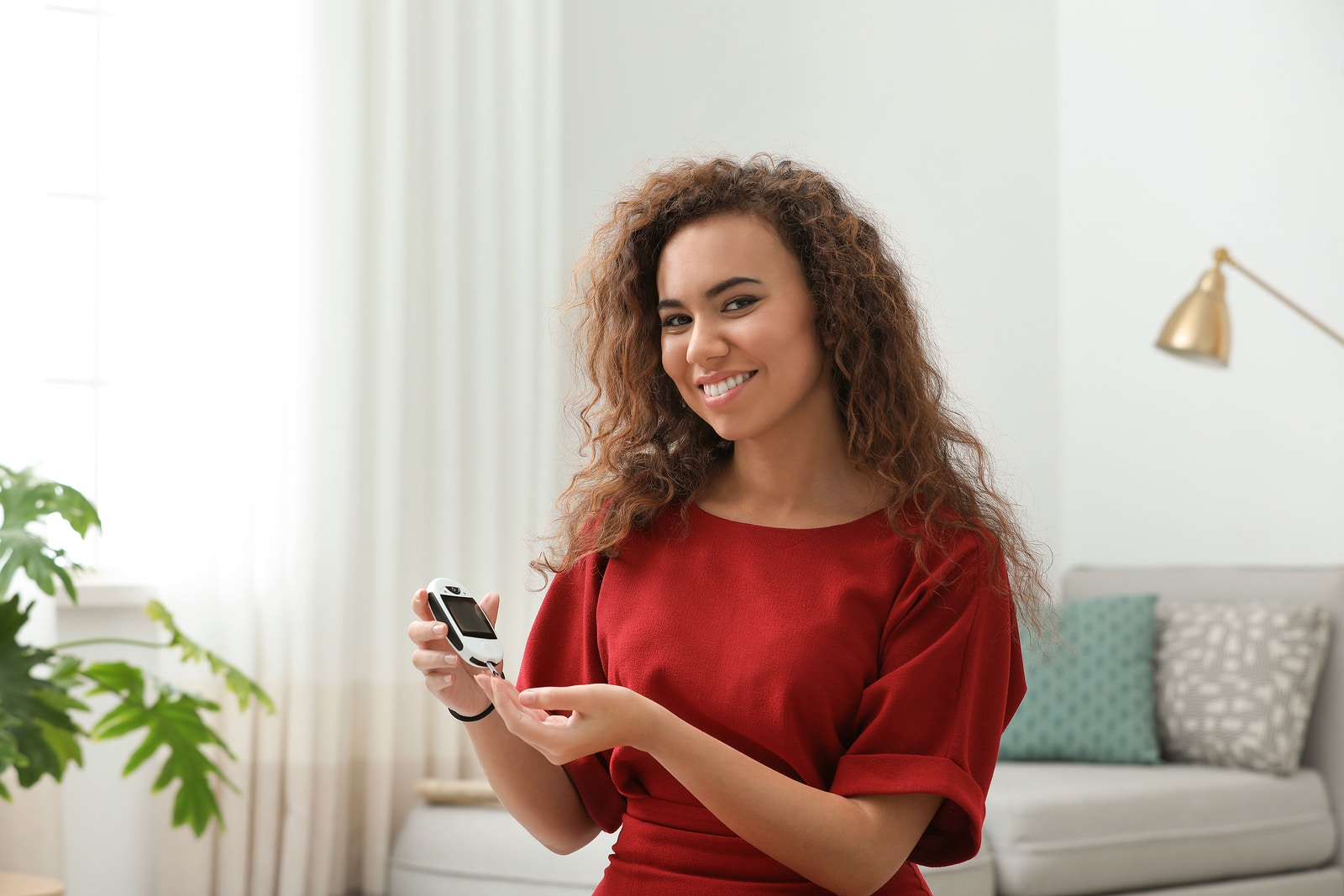
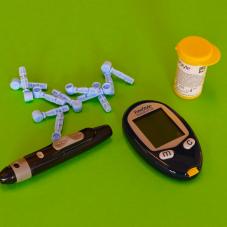
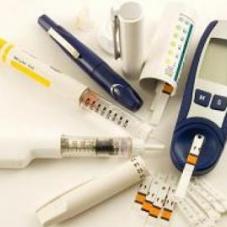
Blood Glucose Monitor
The best way to control your glucose levels is by monitoring them and keeping a record. A blood glucose monitor is a medical device that is used to monitor your glucose levels in the blood-stream. It is quite useful when you need to keep track of your sugar levels and decide whether or not you may need to change your lifestyle.
How does the Blood Glucose Monitor work?
A blood glucose monitor or a glucometer for short is a compact portable device that gives an approximate value of your sugar levels. The device only needs a drop of blood on test stripes, which are then inserted into the monitor and it gives the results.
A glucometer comes with a lancet prick that is usually shaped like a pen. The pen has a needle inside with a spring mechanism so that it can easily penetrate the skin. The test stripes are specially made for obtaining blood samples. They have enzyme electrodes that are used to analyze the blood sample in the monitor.
A glucometer’s lancet usually pricks the thinnest skin layer i.e the fingertips although some glucometers are equipped for Alternate Testing Sites which allow for pricking other parts such as the forearms. More on that later.
The lancet pricks the fingertips to obtain the drop of blood. Sometimes the area is squeezed in order to force the blood out. Then the testing stripes collect the blood sample and are inserted into the monitor which gives a reading on the display. The readings are approximate figures of the glucose levels in the blood-stream.
Alternate Testing Sites
Some glucose monitors are approved for Alternate Testing Sites or ATS for short. Alternate Testing Sites refer to taking the blood sample from another area other than the fingertips.
The fingertips are sensitive to pricks because of the number of nerve cells in the area, therefore a small prick can cause momentary pain. Although some people don’t tolerate it, and for those people, glucometers that are ATS approved are perfect for the job.
Benefits of Glucometer
A glucometer benefits the user in several ways other than finding the glucose levels in the blood-stream. Due to their design, and portability, a glucometer can benefit the user in the following ways:
-
It is convenient to use a glucometer at home or anywhere in order to check the glucose levels.
-
Glucometer doesn’t require any sort of training and is easy to use.
-
Keeps a record of glucose levels on daily basis, and you can keep your sugar in check
-
Evaluate how the medication or the diet is effecting your glucose levels
Glucometer and Diabetes
Those suffering from diabetes must have a glucometer sooner or later. The device is significantly helpful to those suffering from diabetes. Diabetics can monitor their sugar levels and decide whether or not there have been changes in their glucose levels, and that the medication or the exercise is proving helpful. In other words, it can make their lives easier by adjusting their diet, their medication accordingly to the results in the glucometer. This can save their lives from potentially life-threatening complications related to diabetes.










0 Comments